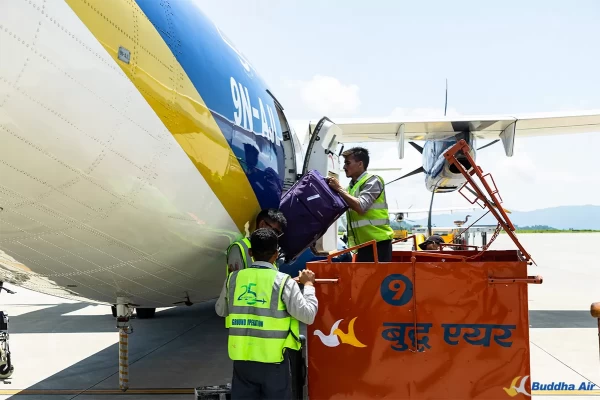
For every aircraft soaring through the sky, maintaining a perfectly balanced load is crucial for smooth and safe flight. Otherwise, even a slight imbalance could cause it to tilt dangerously to one side, leading to instability and potential hazards.
The aircraft load balance is an important factor that determines both the safety and efficiency of every flight. Proper weight distribution directly impacts an aircraft’s stability, manoeuvrability, and fuel efficiency. From the moment an aircraft takes off until it lands, pilots and ground crew must carefully assess the placement of cargo, passengers, and fuel to maintain balance. If an aircraft’s load is improperly distributed, it can lead to serious risks, including difficulty in controlling the aircraft, excessive fuel consumption, and even catastrophic accidents.
In Nepal, where flights frequently operate in challenging terrain with varying weather conditions, maintaining the load balance of aircraft is even more essential. Whether it is a domestic flight or an international route, weight and balance calculations are carefully conducted before every flight.
What is the Load on an Aircraft?
The “load” on an aircraft refers to all the forces and weight it carries during its operation. This includes the aircraft’s structural weight as well as additional components such as passengers, cargo, and fuel. Each of these factors must be accounted for in order to maintain safe flight conditions.
Components of Aircraft Load
Understanding what are the loads of aircraft means understanding how improper weight distribution can lead to instability and flight inefficiencies.
1. Payload
Payload includes passengers, luggage, and cargo. It is the part of the load that generates revenue for commercial airlines and must be properly distributed for optimal flight stability.
2. Fuel Load
Aircraft fuel can significantly impact weight and balance. The amount of fuel carried depends on the flight duration, weather conditions, and fuel efficiency requirements.
3. Structural Load
This refers to the stress and strain acting on the aircraft’s frame during various phases of flight, including takeoff, cruising, and landing.
Also read: Taking a Flight through Different Phases of Flight of an Aircraft
4. Environmental Load
Factors such as wind resistance, turbulence, and air pressure changes also influence how the aircraft responds to weight distribution.
Importance of Aircraft Load Balance in Aviation
The aircraft load balance is more than just a technical requirement—it is a fundamental safety measure that protects passengers, crew, and the aircraft itself. Here’s why load balance is a priority in aviation:
1. Stability and Control
The centre of gravity (CG) of an aircraft determines how it responds to pilot inputs. If the CG is positioned too far forward or too far aft, the aircraft can become unstable, making it difficult to control. Proper balance ensures smooth manoeuvrability during takeoff, cruise, and landing.
2. Fuel Efficiency
An aircraft that is correctly balanced experiences less drag and better aerodynamic performance. This results in optimized fuel consumption, which is especially important for airlines trying to minimize operational costs.
3. Structural Integrity
Uneven weight distribution can exert excessive stress on the aircraft’s frame, leading to long-term structural damage or even catastrophic failure during flight.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Aviation authorities worldwide, including Nepal’s Civil Aviation Authority, have strict guidelines regarding weight and balance. Airlines must comply with these regulations to ensure operational safety and prevent penalties.
What Are the Types of Load in Aircraft?
Aircraft loads can be classified into different categories based on their origin and their effect on the aircraft’s structure and performance.
- Static Loads: Static loads are those that remain constant throughout the flight. This includes the weight of the aircraft’s structure, fixed equipment, and the payload (passengers and cargo).
- Dynamic Loads: Dynamic loads fluctuate due to in-flight movements, including turbulence, turning manoeuvres, and air pressure changes. Pilots and engineers consider these loads when designing and operating an aircraft.
- Aerodynamic Loads: These loads are generated by air resistance as the aircraft moves through the atmosphere. Lift and drag forces must be balanced to ensure smooth and stable flight.
- Impact Loads: Impact loads occur during takeoff, landing, and during turbulence. Proper load distribution helps mitigate stress on the aircraft’s landing gear and frame, ensuring durability and longevity.
You may also like: Air Turbulence: Essential Safety Tips for a Smooth Flight
Conclusion
The load balance of aircraft is one of the most important considerations when it comes to understanding how aviation and flight safety work. Whether it’s a domestic flight in Nepal or an international journey, ensuring proper weight distribution is essential for safety, efficiency, and compliance.
From ground crews carefully arranging luggage in the cargo hold to pilots monitoring fuel loads, every aspect of aviation revolves around achieving the right balance. Nepal’s aviation industry, including airlines like Buddha Air, follows strict weight and balance protocols to ensure smooth and stable flights.
FAQs about Aircraft Load Balance
What Is the Purpose of Weight and Balance?
The primary purpose of weight and balance is to keep an aircraft within safe operational limits. Proper weight and balance calculations help:
- Enhance stability and control during flight.
- Improve fuel efficiency by optimizing aerodynamics.
- Prevent excessive stress on the aircraft’s structure.
- Ensure compliance with aviation safety regulations.
Why Is Balance Important When Loading a Plane?
Balance is crucial when loading an aircraft because an imbalanced load can affect the center of gravity, leading to instability. Some of the risks associated with improper load balance include:
- Difficulty in controlling the aircraft during takeoff and landing.
- Increased fuel consumption due to inefficient aerodynamics.
- Structural damage caused by uneven stress distribution.
By carefully managing the load balance of aircraft, airlines and pilots can avoid these risks and ensure safer, smoother flights.